-
Copper(I)-α-Ketocarboxylate Complexes: Characterization and O2 Reactions That Yield Copper-Oxygen Intermediates Capable of Hydroxylating Arene
S. Hong, S.M. Huber, L. Gagliardi, C.J. Cramer and W.B. Tolman
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 129 (46) (2007), p14190-14192


DOI:10.1021/ja0760426 | unige:3583 | Abstract | Article HTML | Article PDF
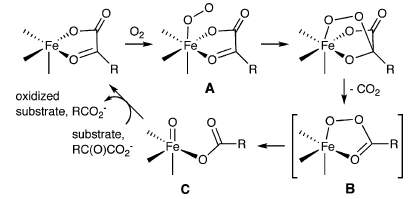
A series of copper(I)−α-ketocarboxylate complexes have been prepared and shown to exhibit variable coordination modes of the α-ketocarboxylate ligand. Reaction with O2 induces decarboxylation of this ligand, and the derived copper−oxygen intermediate(s) has been intercepted, resulting in hydroxylation of an arene substituent on the supporting N-donor ligand. Theoretical calculations have provided intriguing mechanistic notions for the process, notably implicating hydroxylation pathways that involve novel [CuI−OOC(O)R] and [CuII−O-• ↔ CuIII = O2-]+ species.